Products
-
Conscious Breathing Foundation Course
Regular price $250.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
The Relaxator Breath Trainer
Regular price $30.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
Sleep Tape 5M
Regular price $30.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
Book Conscious Breathing
Regular price $25.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
Conscious Breathing Instructor Course
Regular price $450.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
BodyStream
Regular price $2,000.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
CarboHaler
Regular price $700.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
The Conscious Breathing Summit 2022
Regular price $75.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per
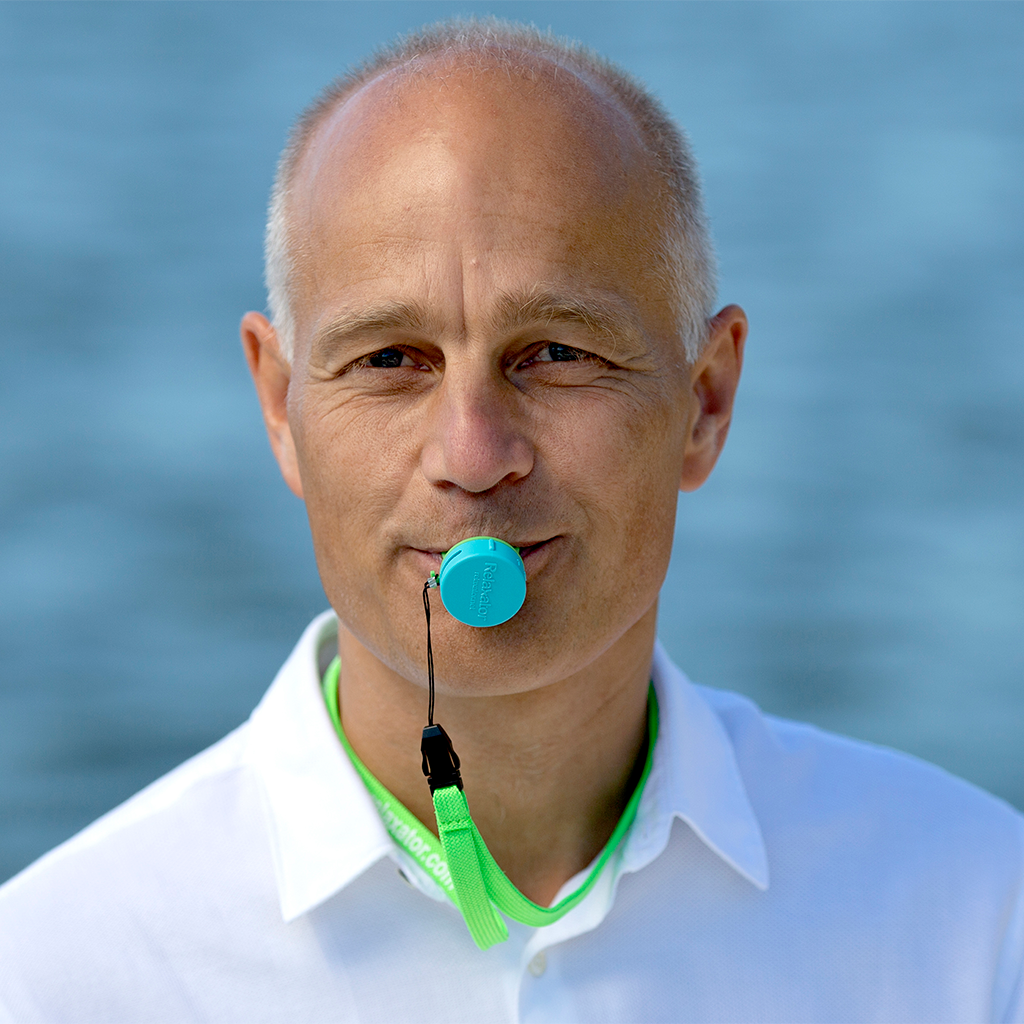

Do you often feel stressed? Do you want to find peace and focus better? Then the Relaxator is for you!
The Relaxator gives you calmer breathing which gives a calmer brain. It immediately reduces your stress and increases your focus and well-being. The Relaxator is extremely easy to use while being very powerful. It can be used basically anytime and anywhere - at work, in the car, before bed, during training, etc. Try it today and increase your well-being too!
The Relaxator takes you to slow, low, relaxed and rhythmic breathing that:
- Increases relaxation, focus and mental clarity
- Balances your nervous system between activity and recovery
- Opens up your airways in the nose, sinuses, throat and lungs
- Strengthens your breathing muscles
- Increases your energy and ability to burn fat

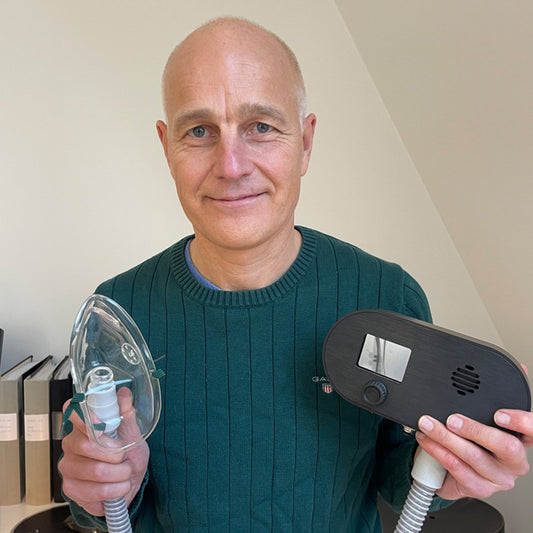
BodyStream
BodyStream is a revolutionary technology allowing you to experience the healing powers of carbon dioxide from the comfort of your own home.

Sanna Ehdin
I am really happy with the Relaxator, because it saves me when I work incredibly hard and especially during evening work. I have a tendency to 'forget' to breathe then, and of course that makes me tired and gives me worse sleep.

James Nestor
When I wrote my New York Times bestseller "Breath" I used the Relaxator all the time. So simple, yet so powerful!